Pratik Rakesh Singh, Mohammadi Zaki, Pankaj Wasnik
30th September 2024
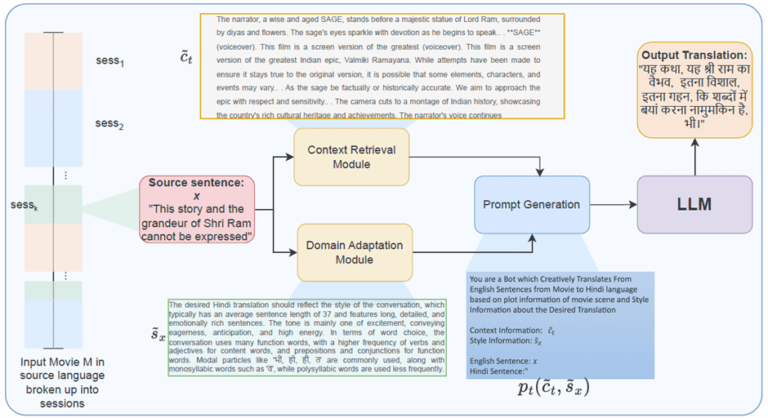
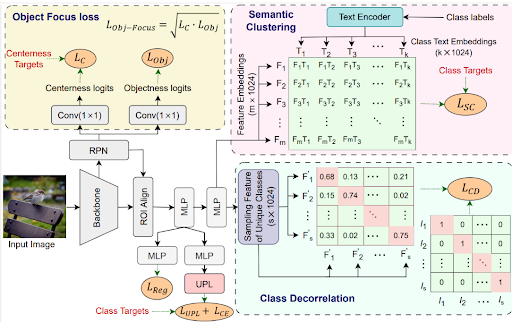
Figure 1. Overview of proposed framework
Mohammadi Zaki summarises paper titled Enhancing Entertainment Translation for Indian Languages using Adaptive Context, Style and LLMs co-authored by Pratik Rakesh Singh, Mohammadi Zaki, Pankaj Wasnik accepted at the 39th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence | February 2025.
In entertainment content, where dialogues often depend on prior interactions to convey a scene’s meaning and emotion effectively, context-aware machine translation plays a vital role. Incorporating the broader dialogue or narrative context, rather than translating sentences in isolation, is crucial to ensure accurate and emotionally relevant translations. On the other hand, entertainment translation also needs a culturally adaptable system to address the challenge of cultural unawareness. Such systems should integrate cultural context for localization to ensure translations are suitable for the intended audience. They should go beyond literal translations, modifying idiomatic expressions, jokes, and cultural references to align with the audience’s customs and values, thereby enhancing the relevance of the translated content.
In this work, we address the challenging task of entertainment translation, where we are given a sequence of source sentences from the entertainment domain without any additional information about the timestamp, speaker ID, or context, and our task is to translate these sentences into dialogues in the target language. The challenge lies in preserving the context, mood, and style of the original content while also incorporating creativity and considering regional dialects, idioms, and other linguistic nuances. The importance of our study is underscored by the need to produce translations that are not only accurate but also engaging for the target audience.
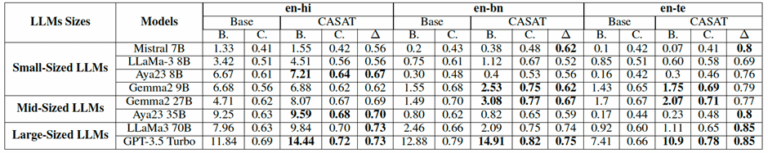
Figure 2. Performance comparison of CASAT with various SOTA LLMs fed with prompts to generate creative translations. Here BU: BLEU, CT: COMET, : Win-ratio of CASAT vs base models.
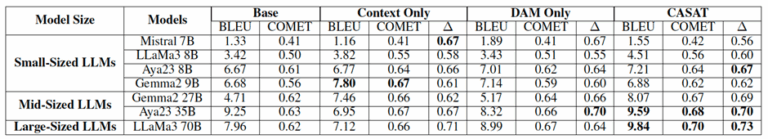
Figure 3. Analysis of individual components of CASAT
We explored the challenging task of entertainment translation, where we identified two key aspects, context, and style, which make this problem unique. We proposed a methodology to estimate these factors and use them to generate context and style-aware translations from an LLM. We showcased the efficacy of our algorithm via numerous experiments using three Indian language entertainment text datasets and various LLMs. Further, our approach has an offline component for partitioning of sessions and generation of contextual information, which we intend to eliminate to develop a completely online algorithm.
To know more about Sony Research India’s Research Publications, visit the ‘Publications’ section on our ‘Open Innovation’s page: Open Innovation with Sony R&D – Sony Research India
In most of the cases, it has been found that Content Driven sessions outperform the time driven sessions. The results are obtained on 6 baselines: STAMP, NARM, GRU4Rec, CD-HRNN, Tr4Rec on datasets like Movielens (Movies), GoodRead Book, LastFM (Music), Amazon (e-commerce).